Toward Generalized ECG-Based Seizure Detection: From Personalized to Cross-Patient Deep Learning Models
Project Details
- Student(s): Hassan Tfaily
- Advisor(s): Dr. Lina Abou Abbas
- Department: Mechatronics
- Academic Year(s): 2024-2025
Abstract
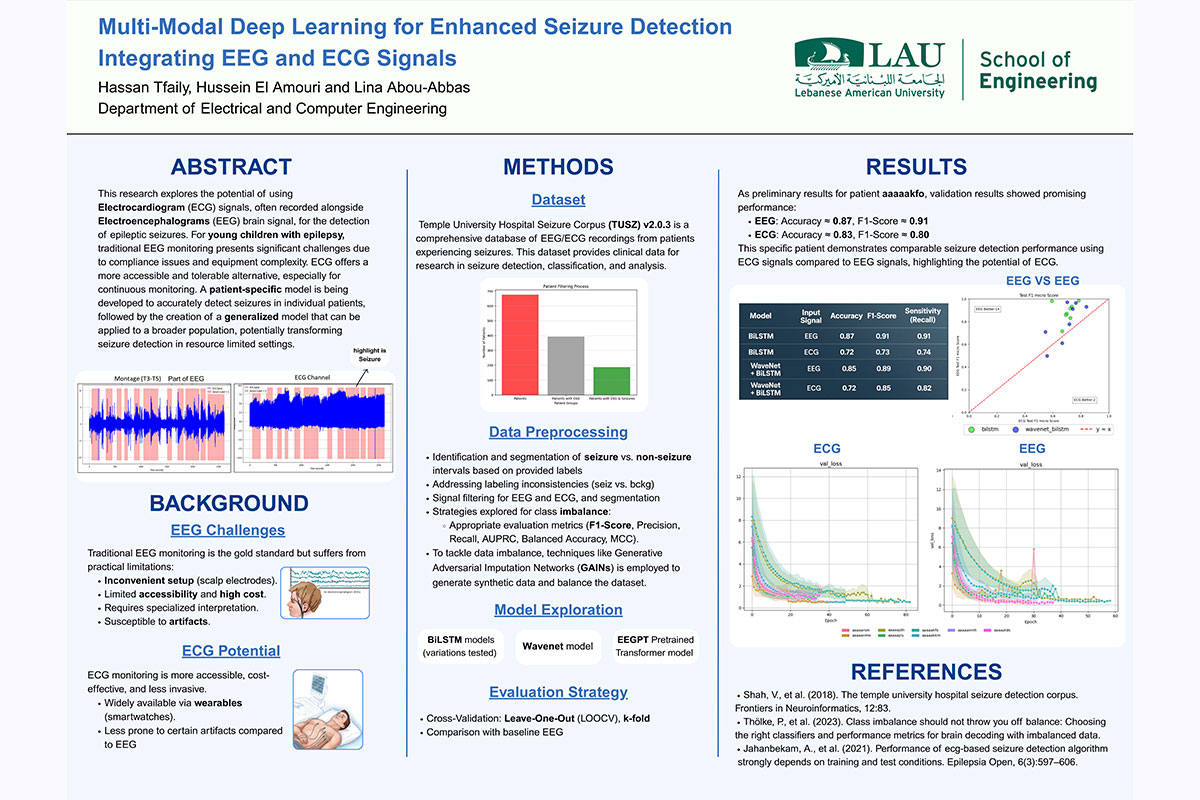
Epileptic seizure detection is critical for patient safety; however, the clinical gold standard, electroencephalography (EEG), is impractical for continuous and long-term monitoring in daily life. Electrocardiography (ECG) presents a promising alternative, offering a noninvasive and portable solution by recording changes in the autonomic nervous system during seizures.
This research presents a two-fold study. First, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of patient specific seizure detection by comparing the performance of models trained on EEG versus ECG signals using BiLSTM and WaveNet-BiLSTM architectures. This initial study confirms the potential of ECG, demonstrating a strong correlation with EEG-based detection.
Based on these findings, we proposed a framework for a generalized cross-patient ECG-based model designed to operate without patient-specific retraining, an essential step towards realworld deployment. Our patient-specific results indicate that while EEG remains superior, ECGbased models achieve comparable performance in several cases, justifying further investigation of robust generalized systems for ambulatory seizure monitoring.
Keywords: ECG, EEG, epileptic seizures, seizure detection, deep learning, BiLSTM, WaveNet, cross-patient model, generalized learning, wearable monitoring